|
ROSE
0.9.6a
|
|
ROSE
0.9.6a
|
Base class for loading a static or dynamic object. More...
#include <BinaryLoader.h>
Classes | |
| class | Exception |
| Base class for exceptions thrown by loaders. More... | |
Public Types | |
| enum | MappingContribution { CONTRIBUTE_NONE, CONTRIBUTE_ADD, CONTRIBUTE_SUB } |
| Describes how a section contributes to the overall memory map. More... | |
| enum | ConflictResolution { RESOLVE_THROW, RESOLVE_OVERMAP, RESOLVE_REMAP, RESOLVE_REMAP_ABOVE } |
| Describes how conflicts are resolved when mapping a section. More... | |
| typedef std::vector< Exception > | FixupErrors |
Public Member Functions | |
| BinaryLoader () | |
| BinaryLoader (const BinaryLoader &other) | |
| virtual | ~BinaryLoader () |
| virtual bool | can_load (SgAsmGenericHeader *) const |
| Predicate determining the suitability of a loader for a specific file header. More... | |
| virtual BinaryLoader * | clone () const |
| Creates a new copy of a loader. More... | |
| void | set_perform_dynamic_linking (bool b) |
| Set whether this loader will perform the linking step. More... | |
| bool | get_perform_dynamic_linking () const |
| Returns whether this loader will perform the linking step. More... | |
| void | set_perform_remap (bool b) |
| Set whether this loader will perform the mapping step. More... | |
| bool | get_perform_remap () const |
| Returns whether this loader will perform the mapping step. More... | |
| void | set_perform_relocations (bool b) |
| Set whether this loader will perform the relocation step. More... | |
| bool | get_perform_relocations () const |
| Returns whether this loader will perform the relocation step. More... | |
| void | set_debug (FILE *f) |
| Set whether this loader will emit diagnostics for debugging. More... | |
| FILE * | get_debug () const |
| Returns whether this loader will emit diagnostics for debugging. More... | |
| void | add_preload (const std::string &libname) |
| Adds a library to the list of pre-loaded libraries. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | get_preloads () const |
| Returns the list of libraries that will be pre-loaded. More... | |
| void | add_directory (const std::string &dirname) |
| Adds a directory to the list of directories searched for libraries. More... | |
| void | add_directories (const std::vector< std::string > &dirnames) |
| Adds directories to the list of directories searched for libraries. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | get_directories () const |
| Returns the list of shared object search directories. More... | |
| virtual std::string | find_so_file (const std::string &libname) const |
| Given the name of a shared object, return the fully qualified name where the library is located in the file system. More... | |
| virtual void | load (SgAsmInterpretation *) |
| Conditionally parse, map, link, and/or relocate the interpretation according to properties of this loader. More... | |
| virtual void | link (SgAsmInterpretation *interp) |
| Links an interpretation by parsing all shared objects required by that interpretation. More... | |
| virtual void | remap (SgAsmInterpretation *interp) |
| Maps sections of the interpretation into the virtual address space. More... | |
| virtual void | fixup (SgAsmInterpretation *interp, FixupErrors *errors=NULL) |
| Performs relocation fixups on the specified interpretation. More... | |
| virtual bool | is_linked (SgBinaryComposite *composite, const std::string &filename) |
| Returns true if the specified file name is already linked into the AST. More... | |
| virtual bool | is_linked (SgAsmInterpretation *interp, const std::string &filename) |
| Returns true if the specified file name is already linked into the AST. More... | |
| virtual std::vector< std::string > | dependencies (SgAsmGenericHeader *) |
| Finds shared object dependencies of a single binary header. More... | |
| virtual void | remap (MemoryMap *, SgAsmGenericHeader *) |
| Remaps the sections for a particular header. More... | |
| virtual SgAsmGenericSectionPtrList | get_remap_sections (SgAsmGenericHeader *header) |
| Selects those sections of a header that should be mapped. More... | |
| virtual rose_addr_t | rebase (MemoryMap *, SgAsmGenericHeader *header, const SgAsmGenericSectionPtrList &) |
| Returns an alternate base virtual address if necessary for remapping. More... | |
| rose_addr_t | bialign (rose_addr_t val1, rose_addr_t align1, rose_addr_t val2, rose_addr_t align2) |
| Calculate adjustment to cause two values to be aligned to two different alignments. More... | |
| virtual MappingContribution | align_values (SgAsmGenericSection *, MemoryMap *, rose_addr_t *malign_lo, rose_addr_t *malign_hi, rose_addr_t *va, rose_addr_t *mem_size, rose_addr_t *offset, rose_addr_t *file_size, bool *map_private, rose_addr_t *va_offset, bool *anon_lo, bool *anon_hi, ConflictResolution *resolve) |
| For a given section, return information about how the section contributes to the memory map. More... | |
| virtual void | addSectionsForRemap (SgAsmGenericHeader *header, SgAsmGenericSectionPtrList &allSections) |
Selects those sections which should be layed out by the Loader and inserts them into the allSections argument. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | register_subclass (BinaryLoader *) |
| Register a loader instance. More... | |
| static BinaryLoader * | lookup (SgAsmGenericHeader *) |
| Finds a suitable loader. More... | |
| static BinaryLoader * | lookup (SgAsmInterpretation *) |
| Finds a suitable loader. More... | |
| static void | load (SgBinaryComposite *composite, bool read_executable_file_format_only=false) |
| Class method to parse, map, link, and/or relocate all interpretations of the specified binary composite. More... | |
| static SgAsmGenericFile * | createAsmAST (SgBinaryComposite *composite, std::string filePath) |
| Parses a single binary file. More... | |
| static int64_t | gcd (int64_t a, int64_t b, int64_t *x=NULL, int64_t *y=NULL) |
| Extended Euclid Algorithm. More... | |
| static SgAsmGenericHeaderPtrList | findSimilarHeaders (SgAsmGenericHeader *matchHeader, SgAsmGenericHeaderPtrList &candidateHeaders) |
Find all headers in candidateHeaders that are similar to matchHeader. More... | |
| static bool | isHeaderSimilar (SgAsmGenericHeader *, SgAsmGenericHeader *) |
| Determines whether two headers are similar enough to be in the same interpretation. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | init () |
| Further initializations in a *.C file. More... | |
Static Private Member Functions | |
| static void | initclass () |
| Initialize the class. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| std::vector< std::string > | preloads |
| Libraries that should be pre-loaded. More... | |
| std::vector< std::string > | directories |
| Directories to search for libraries with relative names. More... | |
| FILE * | debug |
| Stream where diagnostics are sent; null to disable them. More... | |
| bool | p_perform_dynamic_linking |
| bool | p_perform_remap |
| bool | p_perform_relocations |
Static Private Attributes | |
| static std::vector < BinaryLoader * > | loaders |
| List of loader subclasses. More... | |
Base class for loading a static or dynamic object.
The BinaryLoader class is the base class that defines the public interface and provides generic implementations for loading a static or dynamic object. "Loading" means parsing, linking, mapping, and relocating, which are defined as follows:
Some goals of this design are:
The general design is similar to the Disassembler class. The BinaryLoader has class methods to register user-defined loaders with the library and each loader is able to answer whether it is capable of loading a particular kind of binary. ROSE (or any user of this class) can obtain a suitable loader for a particular SgAsmInterpretation, clone it (if desired), modify properties that control its behavior, and use it to load a binary.
Definition at line 43 of file BinaryLoader.h.
| typedef std::vector<Exception> BinaryLoader::FixupErrors |
Definition at line 274 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Describes how a section contributes to the overall memory map.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| CONTRIBUTE_NONE |
Section does not contribute to final mapping. |
| CONTRIBUTE_ADD |
Section is added to the mapping. |
| CONTRIBUTE_SUB |
Section is subtracted from the mapping. |
Definition at line 50 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Describes how conflicts are resolved when mapping a section.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| RESOLVE_THROW |
Throw an exception such as MemoryMap::Inconsistent. |
| RESOLVE_OVERMAP |
Free the part of the original mapping that is in conflict. |
| RESOLVE_REMAP |
Move the section to any unused part of the address space. |
| RESOLVE_REMAP_ABOVE |
Move the section to a higher unused part of the address space. |
Definition at line 58 of file BinaryLoader.h.
|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 90 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References directories, and preloads.
|
inlinevirtual |
Definition at line 97 of file BinaryLoader.h.
|
staticprivate |
Initialize the class.
Register built-in loaders.
|
static |
Register a loader instance.
More specific loader instances should be registered after more general loaders since the lookup() method will inspect loaders in reverse order of their registration.
|
inlinevirtual |
Predicate determining the suitability of a loader for a specific file header.
If this loader is capable of loading the specified file header, then this predicate returns true, otherwise it returns false. The implementation in BinaryLoader always returns true because BinaryLoader is able to generically load all types of files, albeit with limited functionality. Subclasses should certainly redefine this method so it returns true only for certain headers.
Reimplemented in BinaryLoaderElfObj, BinaryLoaderElf, and BinaryLoaderPe.
Definition at line 117 of file BinaryLoader.h.
|
static |
Finds a suitable loader.
Looks through the list of registered loader instances (from most recently registered to earliest registered) and returns the first one whose can_load() predicate returns true. Throws an exception if no suitable loader can be found.
Referenced by Disassembler::disassembleInterp(), Partitioner::disassembleInterpretation(), and SgAsmPESectionTable::parse().
|
static |
Finds a suitable loader.
Looks through the list of registered loader instances (from most recently registered to earliest registered) and returns the first one whose can_load() predicate returns true. This is done for each header contained in the interpretation and the loader for each header must match the other headers. An exception is thrown if no suitable loader can be found.
|
inlinevirtual |
Creates a new copy of a loader.
The new copy has all the same settings as the original. Subclasses that define data methods should certainly provide an implementation of this method, although all they'll need to change is the data type for the 'new' operator.
Reimplemented in BinaryLoaderElfObj, BinaryLoaderPe, and BinaryLoaderElf.
Definition at line 135 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References BinaryLoader().
Referenced by Disassembler::disassembleInterp(), and Partitioner::disassembleInterpretation().
|
inline |
Set whether this loader will perform the linking step.
To "link" means to recursively determine what shared objects are dependencies of the objects already in the AST and to parse them, adding them to the AST also.
Definition at line 147 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References p_perform_dynamic_linking.
Referenced by Disassembler::disassembleInterp().
|
inline |
Returns whether this loader will perform the linking step.
See also, set_perform_dynamic_linking().
Definition at line 150 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References p_perform_dynamic_linking.
|
inline |
Set whether this loader will perform the mapping step.
To "map" a section means to make the section's content available through a MemoryMap object attached to the interpretation that holds the section. This step also resolves conflicts between two or more sections that request overlapping areas of memory.
Definition at line 155 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References p_perform_remap.
Referenced by Disassembler::disassembleInterp().
|
inline |
Returns whether this loader will perform the mapping step.
See also, set_perform_remap().
Definition at line 158 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References p_perform_remap.
|
inline |
Set whether this loader will perform the relocation step.
To "relocate" means to process the relocation sections of an executable and apply "fixups" to parts of memory that have been mapped. The fixups are computed based on the original contents of that memory and the difference in locations from the section's preferred memory location and the location chosen by this loader during the mapping phase. There are many kinds of relocation fixups.
Definition at line 164 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References p_perform_relocations.
Referenced by Disassembler::disassembleInterp().
|
inline |
Returns whether this loader will perform the relocation step.
See also, set_perform_relocations().
Definition at line 167 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References p_perform_relocations.
|
inline |
Set whether this loader will emit diagnostics for debugging.
If the specified file is non-null then diagnostic output is sent to that file; otherwise diagnostic output is disabled.
Definition at line 171 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References debug.
|
inline |
Returns whether this loader will emit diagnostics for debugging.
See also, set_debug().
Definition at line 174 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References debug.
|
inline |
Adds a library to the list of pre-loaded libraries.
These libraries are linked into the AST in the order they were added to the preload list. The libname should be either the base name of a library, such as "libm.so" (in which case the search directories are consulted) or a path-qualified name like "/usr/lib/libm.so".
Definition at line 185 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References preloads.
|
inline |
Returns the list of libraries that will be pre-loaded.
These are loaded before other libraries even if the preload libraries would otherwise not be loaded.
Definition at line 191 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References preloads.
|
inline |
Adds a directory to the list of directories searched for libraries.
This is similar to the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable of the ld-linux.so dynamic loader (see the ld.so man page). ROSE searches for libraries in directories in the order that directories were added.
See also, StringUtility::splitStringIntoStrings().
Definition at line 200 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References directories.
|
inline |
Adds directories to the list of directories searched for libraries.
This is similar to the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable of the ld-linux.so dynamic loader (see the ld.so man page). ROSE searches for libraries in directories in the order that directories were added.
Definition at line 207 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References directories.
|
inline |
Returns the list of shared object search directories.
Definition at line 212 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References directories.
|
virtual |
Given the name of a shared object, return the fully qualified name where the library is located in the file system.
Throws a BinaryLoader::Exception if the library cannot be found.
|
static |
Class method to parse, map, link, and/or relocate all interpretations of the specified binary composite.
This should only be called for an SgBinaryComposite object that has been created but for which no binary files have been parsed yet. It's only called from sage_support.cpp by SgBinaryComposite::buildAST(). A BinaryLoader::Exception is thrown if there's an error of some sort.
Referenced by Disassembler::disassembleInterp().
|
virtual |
Conditionally parse, map, link, and/or relocate the interpretation according to properties of this loader.
If an error occurs, a BinaryLoader::Exception will be thrown. The interpretation must be one that can be loaded by this loader as returned by this loader's can_load() method.
|
virtual |
Links an interpretation by parsing all shared objects required by that interpretation.
In other words, all dependencies of the interpretation are parsed and added to the AST. As mentioned in the BinaryLoader documentation, this process is referred to as "linking".
Recursively perform a breadth-first search of all headers, starting with the headers already in the interpretation. For each header, obtain a list of necessary shared objects (pruning away those that have already been processed) and parse the shared object, adding it to the AST and adding its appropriate headers to the interpretation. Parsing of the shared objects is performed by calling createAsmAST().
This process is recursive in nature. A dynamically linked executable has a list of libraries on which it depends, and those libraries also often have dependencies. The recursion is breadth-first because ELF specifies a particular order that symbols should be resolved. Order is not important for a PE binary since its shared object symbols are scoped to a library.
The list of dependencies for a particular header is obtained by the getDLLs() method, which is also responsible for not returning any shared object that we've already parsed.
Throws a BinaryLoader::Exception if any error occurs.
|
virtual |
Maps sections of the interpretation into the virtual address space.
This function uses the existing MemoryMap attached to the interpretation if it is available, or creates and attaches a new, empty MemoryMap. When using an existing MemoryMap, the map is not cleared. This enables the caller to reserve space in memory.
The mapping algorithms consult each section's preferred address (SgAsmGenericSection::get_mapped_preferred_rva()) and update the section's actual address (SgAsmGenericSection::get_mapped_actual_rva()), adjusting the interpretation's MemoryMap in the process. The algorithms are applied to one binary file header at a time in the order the headers appear in the interpretation. The algorithms may control the order that sections are mapped within any given header.
Subclasses normally don't override this method, but rather the remap() method that is called by this method, namely the remap() that takes a memory map and file header as arguments.
This method throws a BinaryLoader::Exception if an error occurs.
Referenced by Partitioner::disassembleInterpretation().
|
virtual |
Performs relocation fixups on the specified interpretation.
This should be called after sections are mapped into memory by remap(). If an error occurs, then this function either throws the error (BinaryLoader::Exception) or appends it to the errors container (if errors is non-null).
Reimplemented in BinaryLoaderElf.
|
virtual |
Returns true if the specified file name is already linked into the AST.
|
virtual |
Returns true if the specified file name is already linked into the AST.
|
static |
Parses a single binary file.
The file may be an executable, core dump, or shared library. The machine instructions in the file are not parsed–only the binary container is parsed. The new SgAsmGenericFile is added to the supplied binary composite and a new interpretation is created if necessary. Dwarf debugging information is also parsed and added to the AST if Dwarf support is enable and the information is present in the binary container.
|
virtual |
Finds shared object dependencies of a single binary header.
Returns a list of dependencies, which are usually library names rather than actual files. The library names can be turned into file names by calling find_so_file(). Only one header is inspected (i.e., this function is not recursive) and no attempt is made to remove names from the return value that have already been parsed into the AST.
|
virtual |
Remaps the sections for a particular header.
This method is often replaced by subclasses since this is where decisions are made about alignment. Different operating systems and their loaders have different alignment policies.
|
inlinevirtual |
Selects those sections of a header that should be mapped.
Returns the sections in the order they should be mapped.
Reimplemented in BinaryLoaderElf, BinaryLoaderElfObj, and BinaryLoaderPe.
Definition at line 307 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References SgAsmGenericHeader::get_mapped_sections().
|
inlinevirtual |
Returns an alternate base virtual address if necessary for remapping.
For instance, when mapping multiple ELF files, each file should be mapped above a particular address that doesn't conflict with anything that's already mapped. If a new base address is returned, then the remapper will temporarily adjust the base address of the file header for the duration of the mapping operation. The default is to return the current base address.
This method is called with a memory map that describes what has been mapped so far, a file header for the sections that are about to be mapped, and a list of sections about to be mapped.
Reimplemented in BinaryLoaderElf.
Definition at line 318 of file BinaryLoader.h.
References SgAsmGenericHeader::get_base_va().
|
static |
Extended Euclid Algorithm.
The Euclid algorithm for finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two natural numbers, extended to also compute a solution to Bezout's Identity. Bezout's Identity states that if a and b are two non-zero integers with greatest common divisor d, then there exist integers x and y (called Bezout Coefficients), such that 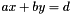 . Additionally
. Additionally d is the smallest positive integer for which there are integer solutions to the preceding equation.
The returned value is the greatest common divisor of a and b. If the caller supplies non-null pointers for x and y then a pair of Bezout Coefficients are returned through those pointers.
| rose_addr_t BinaryLoader::bialign | ( | rose_addr_t | val1, |
| rose_addr_t | align1, | ||
| rose_addr_t | val2, | ||
| rose_addr_t | align2 | ||
| ) |
Calculate adjustment to cause two values to be aligned to two different alignments.
Given two values and two alignments, return the smallest integer adjustment such that subtracting the adjustment from both values results in each value satisfying its alignment constraint.
Note that it is not always possible to find an adjustment. When no adjustment can be found an Exception is thrown.
|
virtual |
For a given section, return information about how the section contributes to the memory map.
The algorithm may use information from the section itself and the memory map as defined up to this point in the mapping process. The main return value is an indication of whether the section adds to the map, subtracts from the map, or does nothing to the map. The remaining arguments are grouped according to their purpose:
malign_lo and malign_hi indicate how the section must be aligned in memory. In particular, the va return value will be a multiple of malign_lo, and the sum of va and mem_size will be a multiple of malign_hi. va value is the low virtual address of the new mapping, and the mem_size is the number of bytes to map. offset value is the byte offset from the beginning of the file in which this section appears, and the file_size is the number of bytes to map from the file into memory. The file_size may be smaller than the mem_size (see below). va_offset is the offset of the section with respect to va (it must be non-negative). The boolean return values anon_lo and anon_hi determine whether ROSE will map file contents (false) or zeros (true) below and above the section when the section is smaller than the mapped region. Zeros are always used for areas that are beyond the end of the file. resolve result indicates what should happen. Subclasses often override this method since each operating system tends to have unique rules about how things are mapped and how conflicts are resolved.
If so desired, the conflict resolution may be handled by the align_values() method itself since the memory map is available there. However, a benefit of allowing a higher layer to resolve the conflict is that diagnostics will be produced automatically when debugging is enabled.
Likewise, this method is allowed to perform the mapping itself if the algorithm in the caller, remap(), cannot be sufficiently influenced by the values that are returned. In this case, this method should perform the mapping and return CONTRIB_NONE to prevent the caller from doing any further mapping.
Reimplemented in BinaryLoaderElf, BinaryLoaderElfObj, and BinaryLoaderPe.
|
virtual |
Selects those sections which should be layed out by the Loader and inserts them into the allSections argument.
The default implementation (in this base class) is to add all sections to the list. Subclasses will likely restrict this to a subset of sections.
|
static |
Find all headers in candidateHeaders that are similar to matchHeader.
This is used to determine whether two headers can be placed in the same SgAsmInterpretation. We make this determination by looking at whether the Disassembler for each header is the same. In other words, an x86_64 header will not be similar to an i386 header even though they are both ELF headers and both x86 architectures.
|
static |
Determines whether two headers are similar enough to be in the same interpretation.
Two headers are similar if disassembly would use the same Disassembler for both. See findSimilarHeaders().
|
private |
Further initializations in a *.C file.
Referenced by BinaryLoader().
|
staticprivate |
List of loader subclasses.
Definition at line 412 of file BinaryLoader.h.
|
private |
Libraries that should be pre-loaded.
Definition at line 413 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Referenced by add_preload(), BinaryLoader(), and get_preloads().
|
private |
Directories to search for libraries with relative names.
Definition at line 414 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Referenced by add_directories(), add_directory(), BinaryLoader(), and get_directories().
|
private |
Stream where diagnostics are sent; null to disable them.
Definition at line 415 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Referenced by get_debug(), and set_debug().
|
private |
Definition at line 417 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Referenced by get_perform_dynamic_linking(), and set_perform_dynamic_linking().
|
private |
Definition at line 418 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Referenced by get_perform_remap(), and set_perform_remap().
|
private |
Definition at line 419 of file BinaryLoader.h.
Referenced by get_perform_relocations(), and set_perform_relocations().