 |
Transport layer protocol provides reliable communication between application software on different hosts.
internet layer handles communications between machines: encapsulates data, routes packets, assembles datagrams, sends error control messeges.
Network interface layer is responsible for accepting datagrams and transmitting them over phusical networks.
 |
| 7. Application | X400 | |
| 6. Presentation | Abstract syntax notation (ASN.1) | |
| 5. session | Packet assemble/disassemble pad | |
| 4. Transport | End.to.end reliability | |
| X.25 | 3. Network | Response to congestion |
| X.25 | 2. Data link | High level datalink communication (HDLC) |
| X.25 | 1. Physical | X.21 : Public networks |
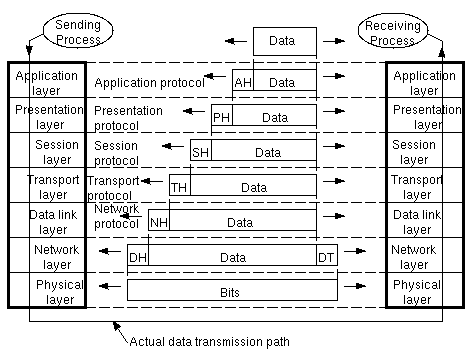 |
An example of how the OSI model is used. Some of the headers may be null. |
 |
The layering principle when a router is used. The frame delivered to router R is exactly the frame sent from host A, but differs from the frame sent between R and B |
 |
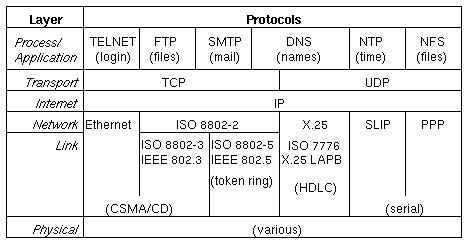
Protocol models and layers |